There are certain diseases whose diagnosis improves if they are detected early. However, if they are allowed to pass, the symptoms may appear when they do not start treatment and their prognosis is but. The so-called "heel test" are tests to detect and be able to treat certain metabolic diseases early.
The neonatal screening, neonatal screening or heel test is a blood test that aims for a very early diagnosis of diseases that have a very good prognosis if detected early, such as hypothyroidism, phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis ... If these diseases were diagnosed late, we could talk of serious complications, even irreversible in certain cases.
That is why the heel test is so important in newborns, all are performed in the hospital environment and thus the test is a very important preventive prick.
Diseases detected by the heel test
As we have commented, neonatal screening is a metabolic test, and within all metabolic diseases, those that are more frequent and that have a treatment that considerably improves the prognosis of the disease are sought if applied early.
These metabolic diseases are characterized by a malfunction of the internal chemistry of the body (metabolism), which results in an increase or a lack of certain substances. The consequences would be a malfunction of various organs (depending on the type of disease can be the heart, liver, lungs ...), alterations in brain development and mental retardation and growth and development disorders or anemia. Most of these diseases have a genetic basis and are inherited, although not suffered by parents.
 In Babies and more Breastfeeding to reduce pain caused by heel testing and vaccinations
In Babies and more Breastfeeding to reduce pain caused by heel testing and vaccinations However, Depending on the country and even the autonomous community and the different protocols, the diseases sought by the test are not the same. In Spain, the detection of phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism is included in all metabolic screening programs. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and congenital adrenal hyperplasia are also included in many communities.
In three communities there is a screening program for congenital hemoglobinopathies, which are diseases that occur at birth and cause anemia. Some communities have analysis technologies such as mass spectometry, which allow to detect many more metabolic diseases.
Hyperphenylalaninemias, galactosemia, biotinidase deficiency, maple syrup disease, homocystinuria, beta-oxidation defects of medium-chain fatty acids and tyrosinemia are other metabolic diseases that are detected in the heel test in different European countries.

When and how the heel test is done
The heel test is performed by puncturing the baby's heel with a lancet, a surgical instrument to make small incisions. It is a sample of capillary blood, that is, taken superficially, it is not a deep incision. The heel is compressed a little by the part of the puncture and blood is allowed to drip, impregnating a special absorbent paper that will be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
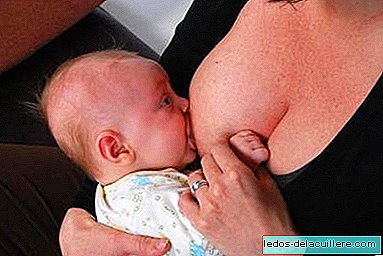
The test is annoying and can hurt the baby. To relieve that pain, nothing better than "tetanalgesia", breastfeeding while the puncture is performed, being in contact with the baby. If this is not possible, the AEP recommends administering a solution of sugar water and always contacting the mother, talking to her, caressing her.
According to the different programs, one or two tests are usually done. You can ask your hospital or the midwife what is the exact procedure in your case and what diseases are detected in your community or region.
The Commission of Congenital Metabolic Errors of the Society of Clinical Biochemistry and Molecular Pathology recommends that, as a general rule, blood collection from the heel should be performed as soon as possible after 48 hours of life. Recommends two strategies according to the different geographical and infrastructure conditions of each autonomous community in order to guarantee 100% coverage of newborns in their area:
Single extraction. From 48 hours of life of the newborn, with established protein feeding, obtaining a single sample for the detection of hypothyroidism, phenylketonuria and congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Double extraction. The first extraction after 48 hours of life, before hospital discharge, for the detection of hypothyroidism and congenital adrenal hyperplasia and the second after the fifth day of life for the detection of phenylketonuria.
 In Babies and more When the heel test is positive: interview with Patricia Lorente, mother of a girl with phenylketonuria
In Babies and more When the heel test is positive: interview with Patricia Lorente, mother of a girl with phenylketonuriaIn some countries a test is performed between 48 hours and 72 hours of the child. The optimal moment of obtaining the sample is controversial and therefore we observe these differences.
Together with the collection of the blood impregnated in paper, the family and baby data are collected in a file that, later, will be used to send the results obtained and contact the parents if necessary.
If the heel test is positiveIt will be repeated to verify that there is no error and if a metabolic disease is finally confirmed, the treatment will be initiated and the parents will be guided by genetic advice about whether the successive children can suffer from the same problem.
Definitely, The heel test is a test that is performed on the newborn and can reduce complications and save the baby's life. All newborns are entitled to this free study, which is carried out in all hospitals and, although we are sorry that they have to prick him, so tiny, it is highly recommended to prevent.
Photos | iStock
More information | AEPED, Salut Channel
In Babies and more | The heel test a preventive prick, The heel test in newborns