The premature births, those that occur before the 37th week of gestation, have increased markedly in the last decade. Although they only represent 10 percent of births, the mortality rate is high, as well as the complications that can result in the baby being born too early.
Many couples believe that premature birth is just a matter of luck (or bad luck), which simply "touches." While it is true that premature birth cannot always be avoided, there are risk factor's that knowing them can take the necessary measures to reduce the chances of suffering.
In an earlier post we talked about the warning signs of preterm birth. Now we will take care of the risk factors related to preterm birth, most unlikely to avoid, but also what the future mom can do to avoid, or at least minimize, the risks of a birth before term.
Risk factors for premature delivery
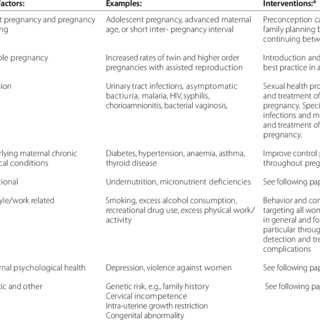
There are certain situations that increase the risk that the pregnancy does not reach term, such as:
AdvertisingPreeclampsia: It is a gestation disorder that develops in the second half of pregnancy characterized by an increase in blood pressure.
Diseases of the mother: kidney diseases, diabetes, heart disease or infections.
Multiple pregnancy: most twin pregnancies result in preterm labor.
Complications of the placenta such as placenta previa or placental abruption.
Problems in the uterus as structural defects.
Having had a threat of premature birth or a previous premature delivery.
Little time difference (less than a year) between pregnancies.
The mother's age: being under 18 or over 40 during pregnancy.
Assisted reproduction techniques: they are related to a higher risk of multiple births
Genetic factors: Women who have a mother, sister or half-sister (from the same mother) who have had a preterm birth are 60 percent more likely to have a baby prematurely.
How to avoid preterm birth
Wear a healthy pregnancy.
To practice moderate exercise before and during pregnancy: physically active women reduce the risk of giving birth prematurely.
Take care of food during pregnancy: avoid caffeine, foods rich in sugars and fats, increase the consumption of fruits and vegetables, stay hydrated.
Do not consume alcohol, drugs, medications, or smoke.
Go to all prenatal consultations, even if you are well.
Control weight gain: excessive weight gain during pregnancy is related to increased risk of preterm birth
Avoid stress situations as much as possible at work and at home: the important thing right now is your baby. Stress and anxiety of the mother have a negative impact on the development of the fetus.
Take care of environmental environment of the pregnant woman: avoid exposure to contaminants as much as possible.
Find out about the warning signs of preterm birth to know how to recognize them if they occur. Identifying them in time can prevent labor from occurring.