Among the prenatal tests that we have been commenting on in these weeks, chorionic biopsy and cordocentesis are the most invasive, the ones that involve the most risks and those that are carried out lastly when making a diagnosis.
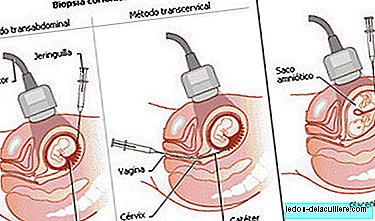
Chorionic biopsy involves removing a chorionic villus sample which are structures that are part of the tissue that gives rise to the placenta and when analyzed can be considered equivalents as if we were taking tissue from the fetus.
The technique consists of introducing a needle through the cervix (transcervical) or through an abdominal puncture with local anesthesia (transabdominal), while an ultrasound is performed, which allows to visualize the maternal and fetal structures to ensure that Biospia is done well and without problems.
Both techniques are equally safe and effective, although the rates of spontaneous abortion are slightly higher when done through the cervix. The choice of one or the other is made according to the location of the placenta, the time of gestation and the experience of the doctor.
It is especially indicated when an increased nuchal translucency or malformation is detected on the first trimester ultrasound. It is usually recommended in these cases, being always optional:
- If the mother is 35 years old or older: because it increases the probability of giving birth to a child with a congenital defect.
- Previous child or pregnancy with any chromosomal or other disorder.
- Family history of genetic defects.
- When some other abnormality is detected in other prenatal tests.
- When there is a real possibility of risks and one does not want to wait for amniocentesis to contemplate the possibility of abortion.
It has to be done between 10-12 weeks of gestation. The advantage of this test is that it is a rapid technique, which allows to know very soon if the fetus has any genetic abnormality, long before the amniocentesis. The material obtained is analyzed to study the DNA, chromosomes and enzymes of the fetus.
On other occasions, it is also performed as an alternative to amniocentesis to be able to study the baby's karyotype. It is the most useful technique to detect chromosomopathies such as Down syndrome. The effectiveness in obtaining a diagnosis is 99.7%. It does not detect neural tube defects such as spina bifida, to detect it an amniocentesis must be performed.
Once done, the results take between 2 days and 14 days, depending on the technique used. The duration of the technique is five minutes, once the patient is prepared.
Risks: It has an abortion rate of 0.6-0.9% (higher than amniocentesis). A slight discomfort is felt by the vaginal method as in a vaginal cytology and there may be a little bleeding after performing the procedure. It requires neither previous preparation nor hospitalization.
In Babies and more | Special pregnancy In Babies and more | All prenatal tests